1. Magnetic Characteristics of VACODUR 49
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Saturation Polarization (Js) | Up to approx. 2.3 T — significantly higher than silicon steel |
| Coercivity | Low coercive force for reduced hysteresis losses |
| Core Loss | Moderate to low, depending on lamination thickness & annealing |
| High Electrical Resistivity | Improves performance at medium–high frequencies |
| Annealing Sensitivity | Heat treatment strongly influences magnetic performance |

2. Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics
| Property | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Yield Strength (post‑annealing adjustable) | Can be tuned for high‑speed rotors using specific annealing cycles |
| High Tensile Strength | Suitable for mechanically stressed rotor stacks |
| Thermal Stability | Operates reliably over elevated temperatures |
| Fatigue Resistance | Good fatigue endurance for cyclic‑load motors |

3. ✨Advantages in Electric Motors
- Higher magnetic loading allows smaller and lighter stator/rotor designs.
- Improved torque density and power density in compact robot joint motors.
- Reduced magnetic saturation risk at high current / high flux operation.
- Suitable for high‑speed rotors where mechanical strength is critical.
- Supports precision applications in robotics, aerospace, and servomotors.

4. Limitations & Considerations
- More expensive than standard Si‑Fe steel sheets.
- Requires controlled annealing to achieve optimal magnetic performance.
- Must ensure proper insulation coating when used as laminations.
- Not recommended as structural housing material (magnetic core only).
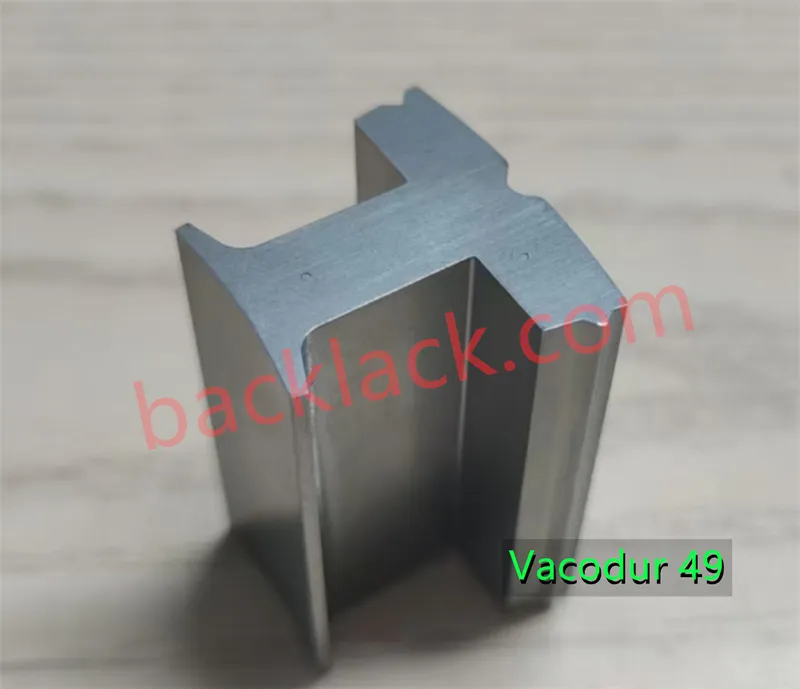
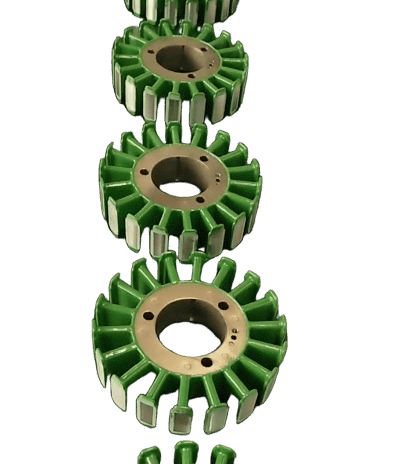
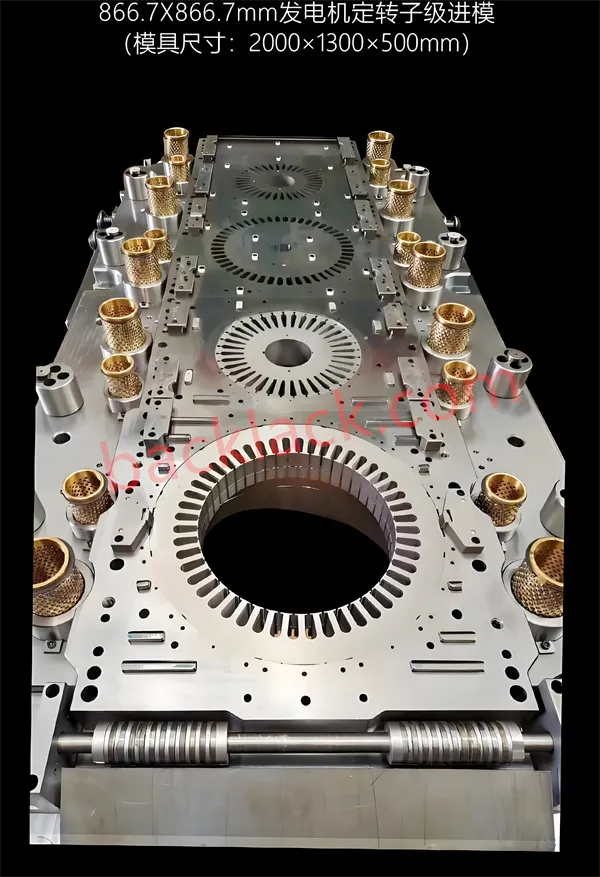
5. Custom Magnetic Core Manufacturing Using VACODUR 49
VACODUR 49 is commonly used for advanced motor and generator cores where magnetic flux density and rotor strength are critical. Custom fabrication includes:
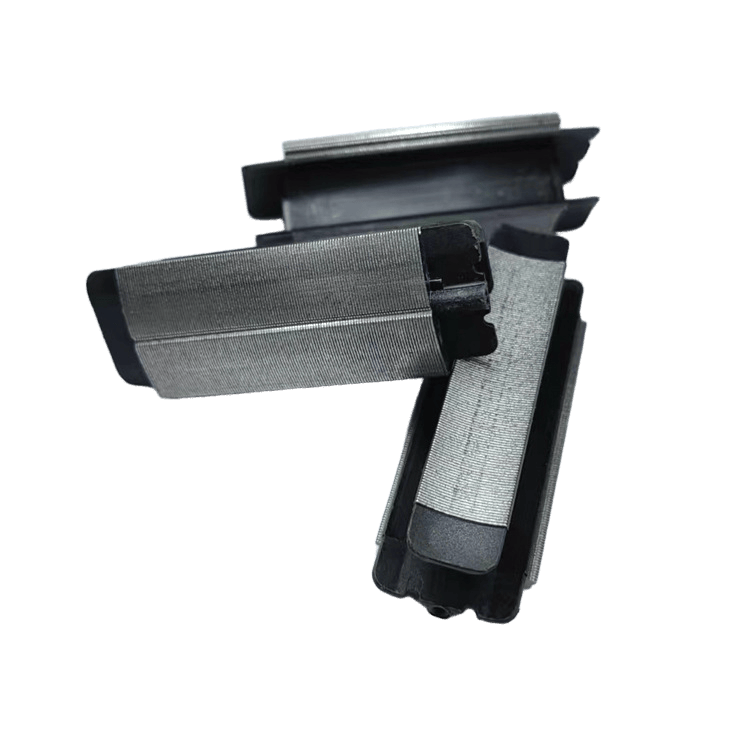
- Laser‑cut or stamped laminations
- Rotor & stator lamination stacks
- Segmented motor cores
- Axial flux motor plates
- High‑speed rotor components
Typical Engineering Steps
- Material selection:Determine required flux density and mechanical limits.
- Lamination thickness optimization:0.1–0.35 mm depending on speed/frequency.
- Precision stamping or laser cutting:Controls dimensional tolerances.
- Annealing:Recrystallization to maximize permeability and saturation.
- Stack bonding:Welding, bonding, interlocking, or epoxy insulation.

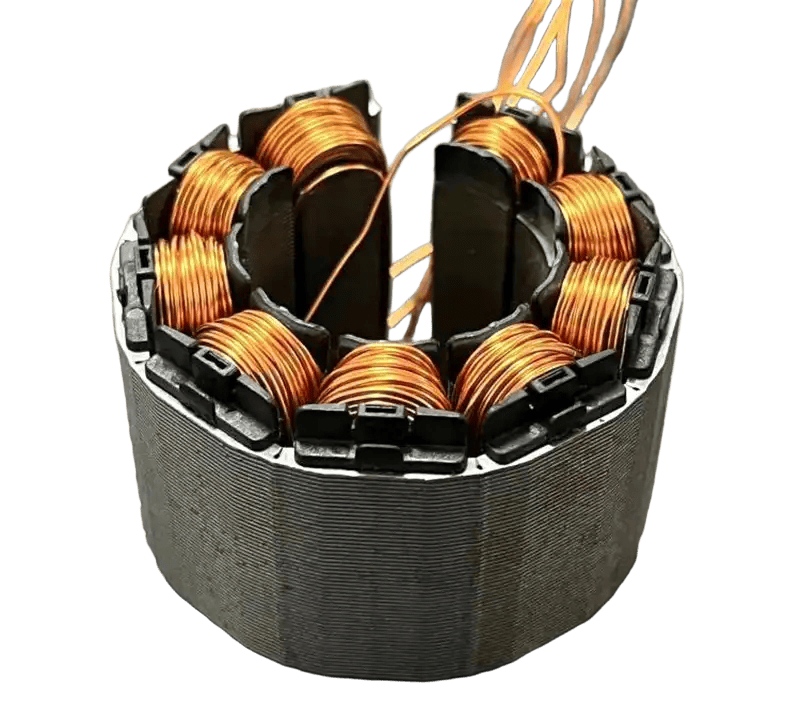
6. Recommended Motor Applications
- Robot joint motors (high torque density)
- High‑speed PMSM / BLDC rotors
- Aerospace actuators
- Precision servo motors
- Axial flux motors
7. Engineering Summary
VACODUR 49 is a premium Co‑Fe alloy suited for advanced electric motor applications where high saturation flux density and structural integrity are essential. Its use can substantially increase torque density and reduce motor size, particularly beneficial for compact robotic joints and high‑performance servo systems. Proper processing—especially annealing and lamination construction—is critical to achieving full performance.
About Youyou Technology
Youyou Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the manufacture of Self-bonding precision cores made of various soft magnetic materials, including Self-bonding silicon steel, ultra-thin silicon steel, and Self-bonding specialty soft magnetic alloys. We utilize advanced manufacturing processes for precision magnetic components, providing advanced solutions for soft magnetic cores used in key power components such as high-performance motors, high-speed motors, medium-frequency transformers, and reactors.
The company Self-bonding precision core products currently include a range of silicon steel cores with strip thicknesses of 0.05mm(ST-050), 0.1mm(10JNEX900/ST-100), 0.15mm, 0.2mm(20JNEH1200/20HX1200/ B20AV1200/20CS1200HF), and 0.35mm(35JNE210/35JNE230/ B35A250-Z/35CS230HF), as well as specialty soft magnetic alloy cores including Hiperco 50 and VACODUR 49 and 1J22 and 1J50.