Motor lamination technology: the invisible force driving modern industry
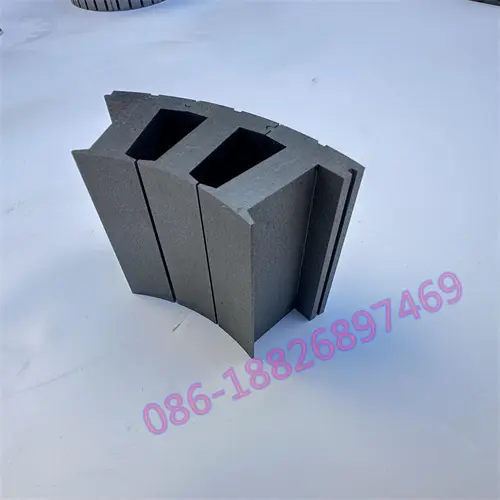
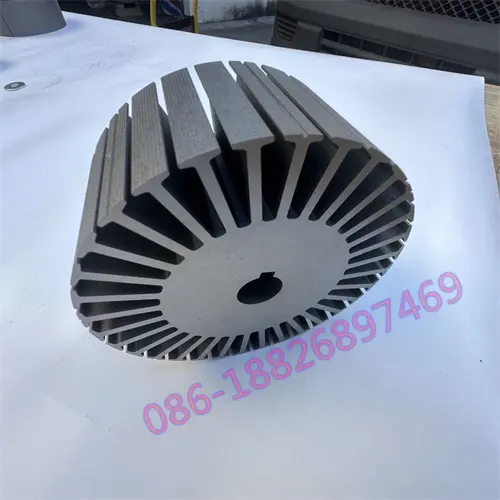
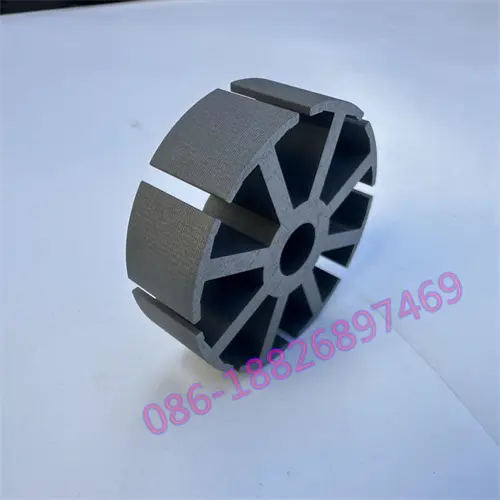
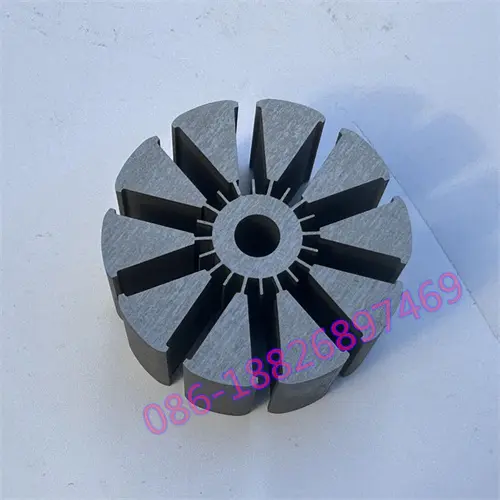
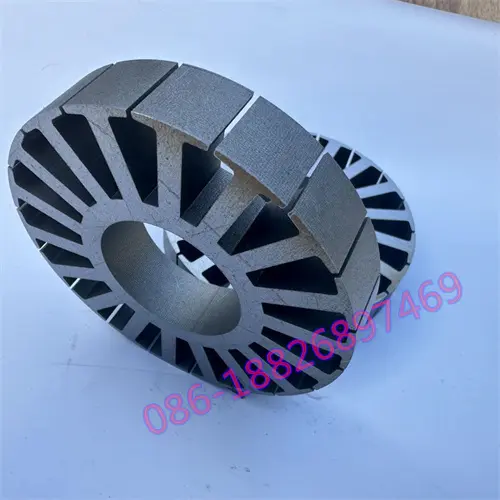
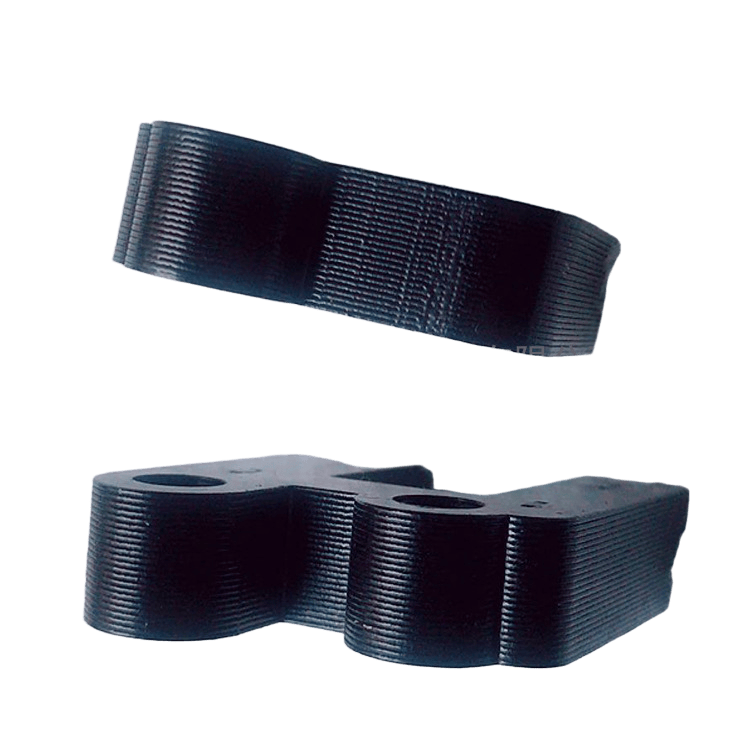
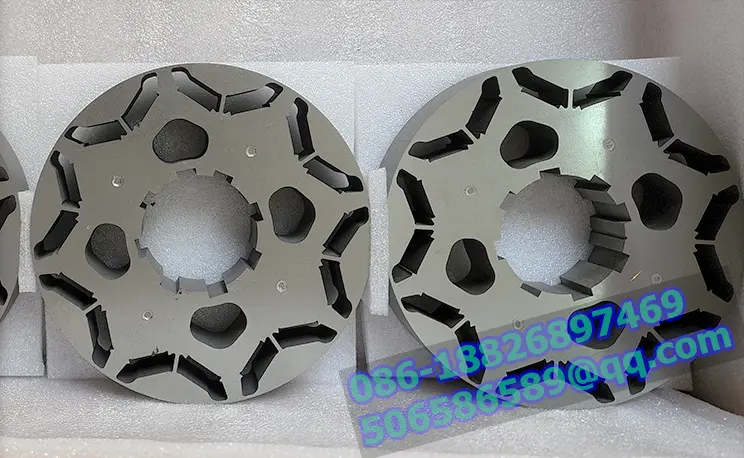
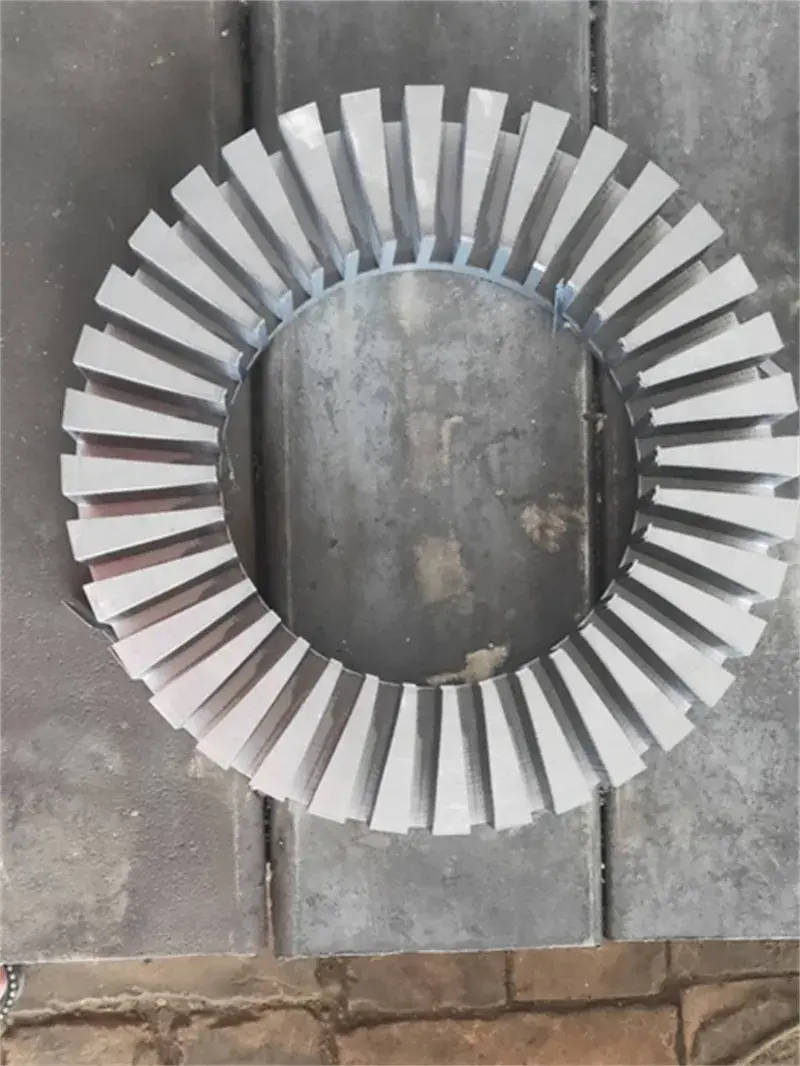
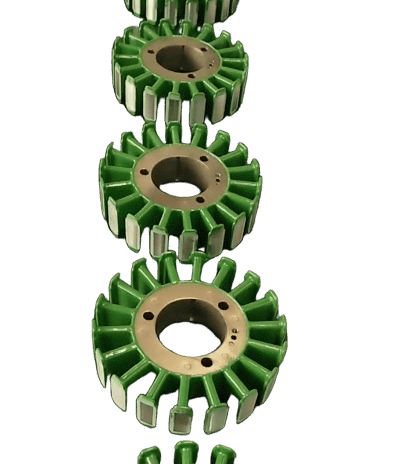
Motor laminations, the structural foundation of the motor's heart, consist of layers of finely stacked metal sheets designed to maximize electrical and magnetic performance. These laminates are widely used in automotive, electronics, renewable energy, medical equipment and other fields, and are a key factor in promoting technological innovation and energy efficiency improvements.
Adhesive technology: flexible and efficient art of material fusion
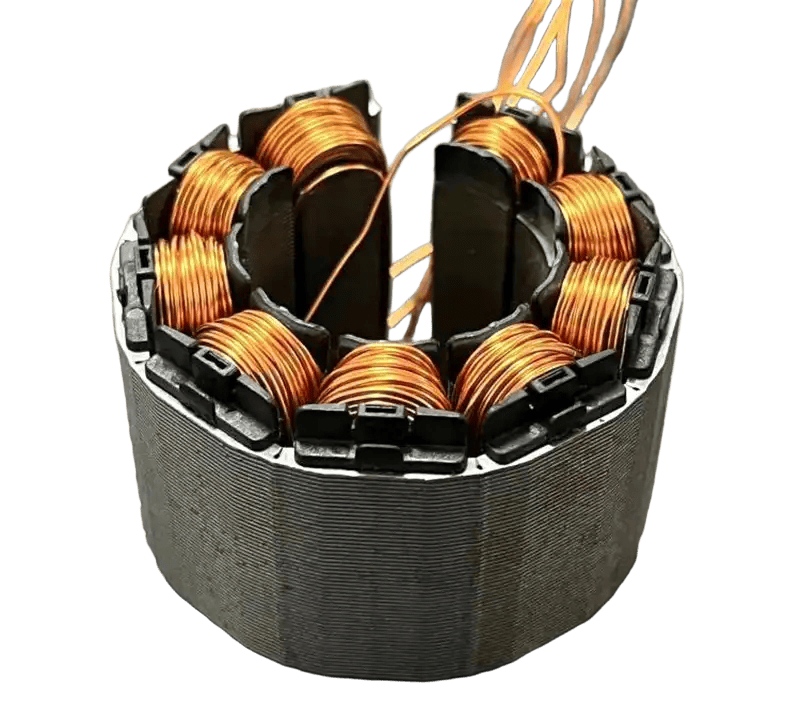
Bonding, where laminations are securely bound together with adhesives, is favored for its broad material compatibility, cost-effectiveness and ability to reduce weight. Not only does it work with metals, it also combines perfectly with composites and polymers, opening up new avenues for design innovation. Bonding technology is excellent at reducing vibration and making motors run smoother, especially in weight-sensitive applications such as aerospace and portable electronics. However, the long-term stability of the bond and the initial cure time are important considerations for manufacturers.
Welding technology: powerful and precise structural integration
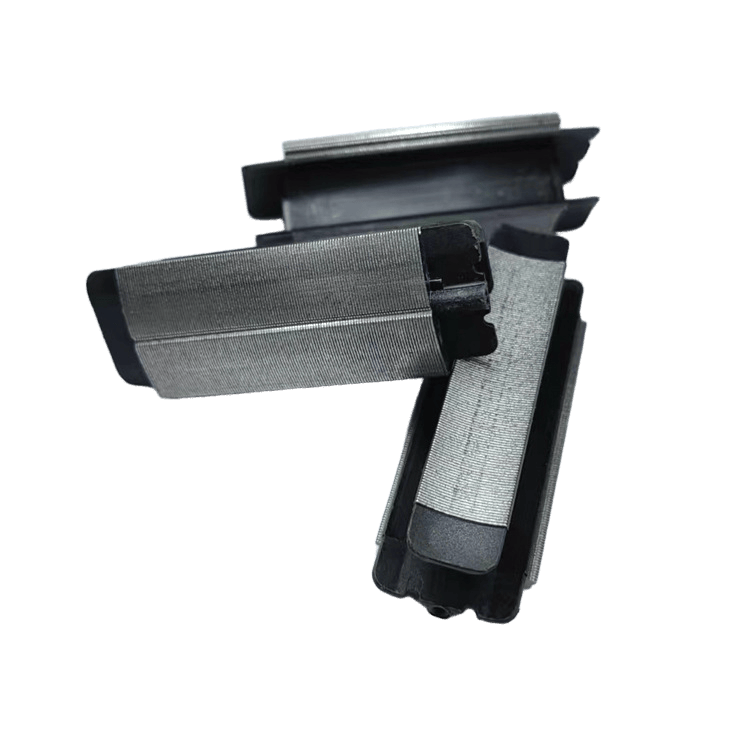
In contrast, welding uses heat and pressure to seamlessly fuse laminate materials to create an extremely strong structure. From the precision of laser welding to the wide application of TIG and MAG welding, welding technology ensures the high strength and durability of motor laminations, especially playing a central role in applications that require extreme reliability and efficiency, such as electric vehicles and industrial motors. Although welding technology is superior in improving production efficiency, its high initial investment, complex operating requirements, and possible deformation of thin materials are challenges that cannot be ignored when making decisions.
Decision-making orientation: comprehensive consideration, precise selection
Deciding between bonding and welding requires a combination of factors: material properties, cost control, production speed and environmental impact. Although welding is superior in strength and durability, bonding is more attractive in terms of flexibility, cost-effectiveness and material variety. In addition, the urgency of production efficiency and the ultimate goal of the project are also important considerations.
Conclusion
In short, understanding the nuances of bonding and welding in motor lamination technology is the key to optimizing the manufacturing process and ensuring product performance. As technology continues to evolve, manufacturers need to keep up with trends and continually evaluate innovative technologies to ensure they remain competitive in the rapidly changing field of lamination manufacturing. Whether it is automotive motors pursuing ultimate performance, or renewable energy equipment requiring lightweight and high efficiency, accurately grasping the applicable scenarios of bonding and welding is a key step towards industry leadership.
About Youyou Technology
Youyou Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the manufacture of backlack precision cores made of various soft magnetic materials, including backlack silicon steel, ultra-thin silicon steel, and backlack specialty soft magnetic alloys. We utilize advanced manufacturing processes for precision magnetic components, providing advanced solutions for soft magnetic cores used in key power components such as high-performance motors, high-speed motors, medium-frequency transformers, and reactors.
The company Self-bonding precision core products currently include a range of silicon steel cores with strip thicknesses of 0.05mm(ST-050), 0.1mm(10JNEX900/ST-100), 0.15mm, 0.2mm(20JNEH1200/20HX1200/ B20AV1200/20CS1200HF), and 0.35mm(35JNE210/35JNE230/ B35A250-Z/35CS230HF), as well as specialty soft magnetic alloy cores including Soft Magnetic Alloy 1J22/1J50/1J79.