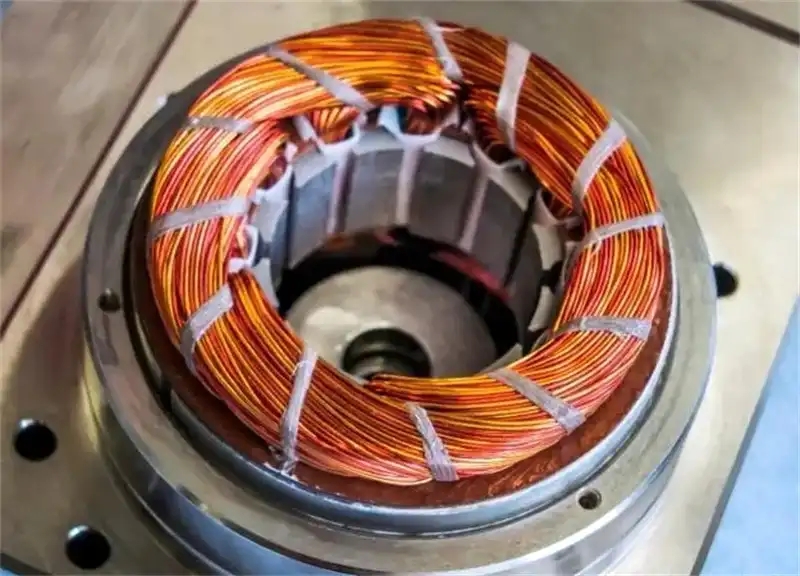
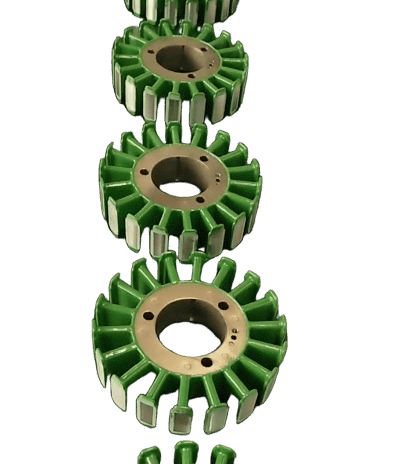
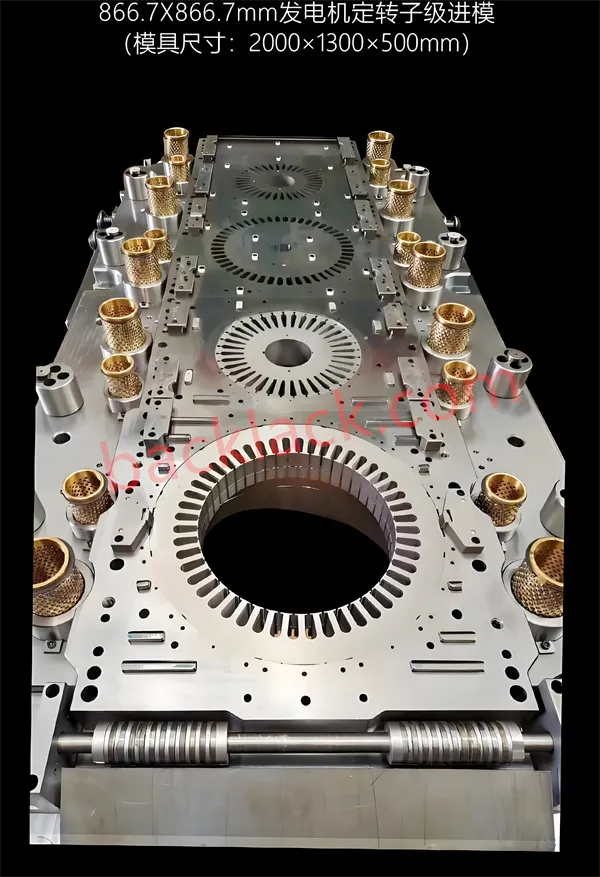
Technology Disruption: Physical Limits of Traditional Cores and Breakthrough of Self-Adhesive Technology
The evolution of motor cores is essentially a history of battling energy loss versus mechanical stress. Each rivet point left on a traditional core creates a zone of localized magnetic domain distortion, increasing eddy current loss by over 15%. The heat-affected zone from welding causes irreversible changes to the silicon steel's crystal lattice structure, reducing permeability and causing iron loss to spike dramatically.
More critically, in the ultra-high-speed realm above 20,000 RPM, centrifugal force creates a micron-level tendency for separation between laminations, leading to decreased dynamic stiffness and an exponential increase in vibration and noise. The breakthrough of self-adhesive technology lies in its use of molecular-level adhesive force to replace mechanical connections, eliminating physical failure points. The adhesive forms a uniform nano-film between sheets, creating a "rigid yet flexible" quasi-monolithic structure upon curing—providing sufficient overall rigidity to resist centrifugal force while retaining appropriate damping characteristics to absorb vibrational energy.
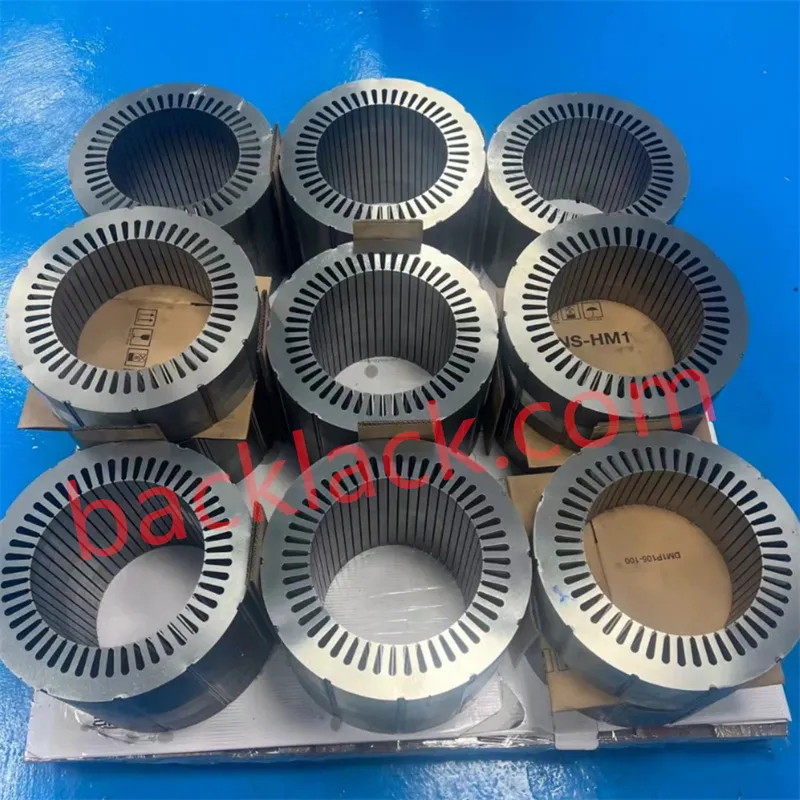
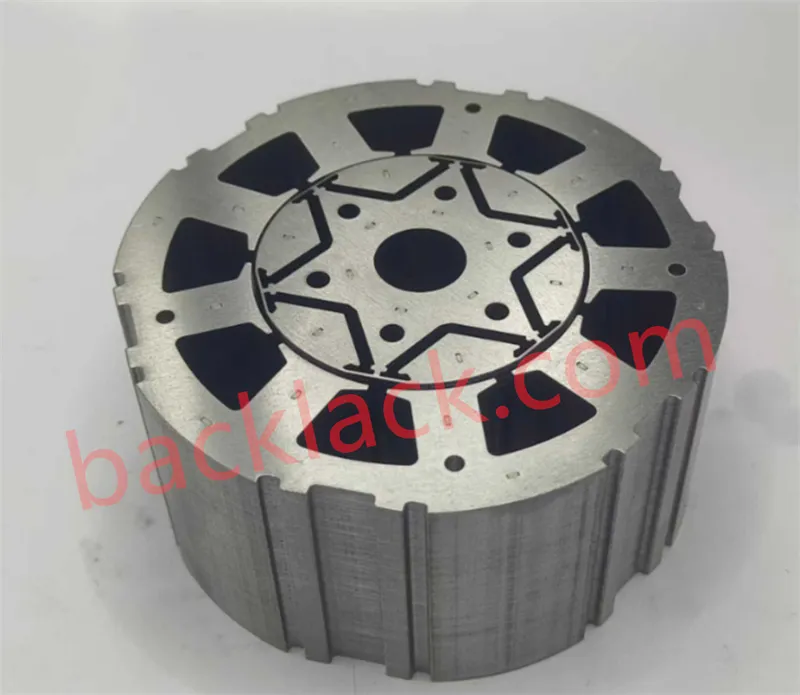
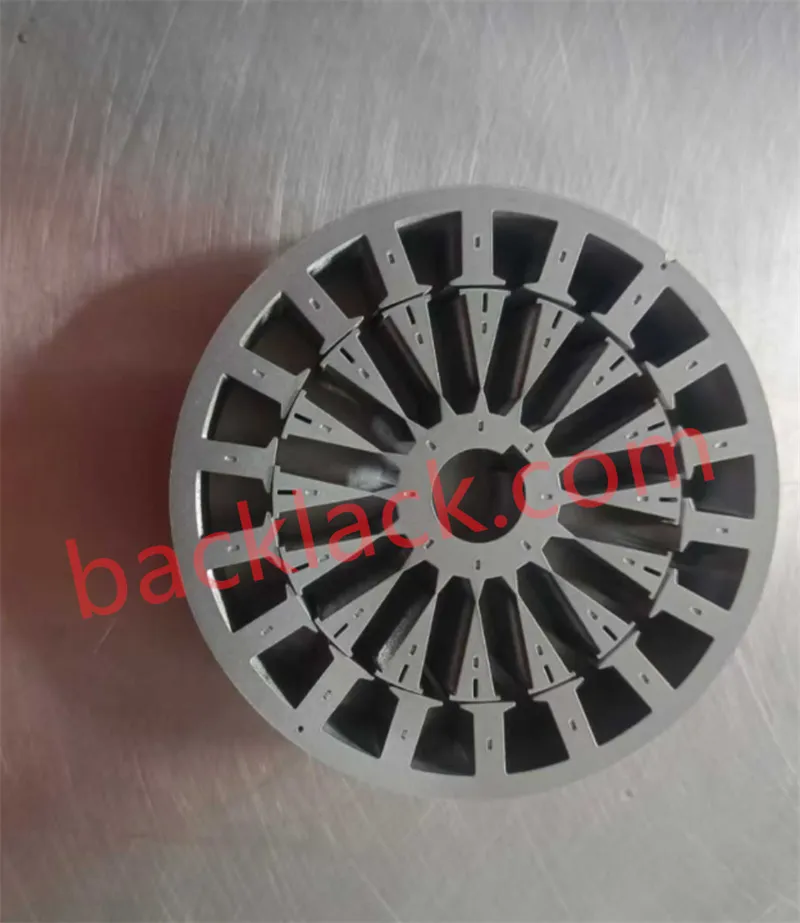
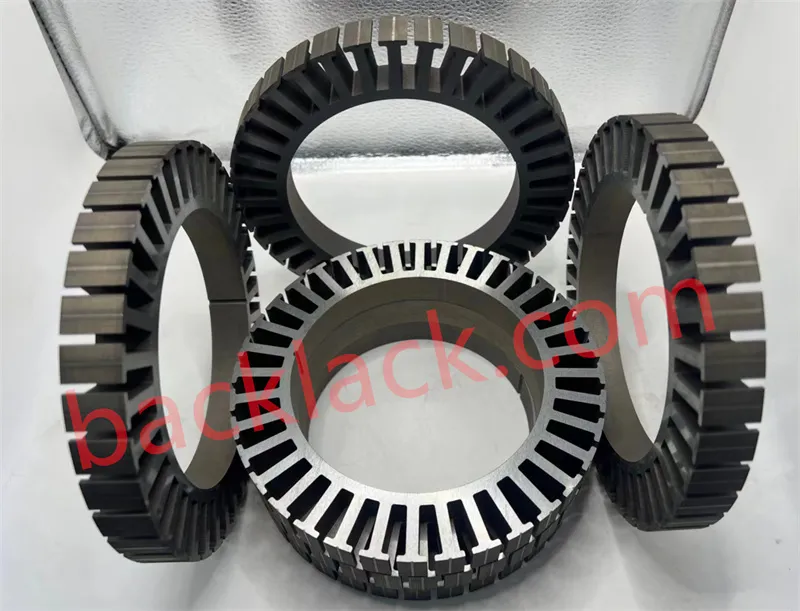
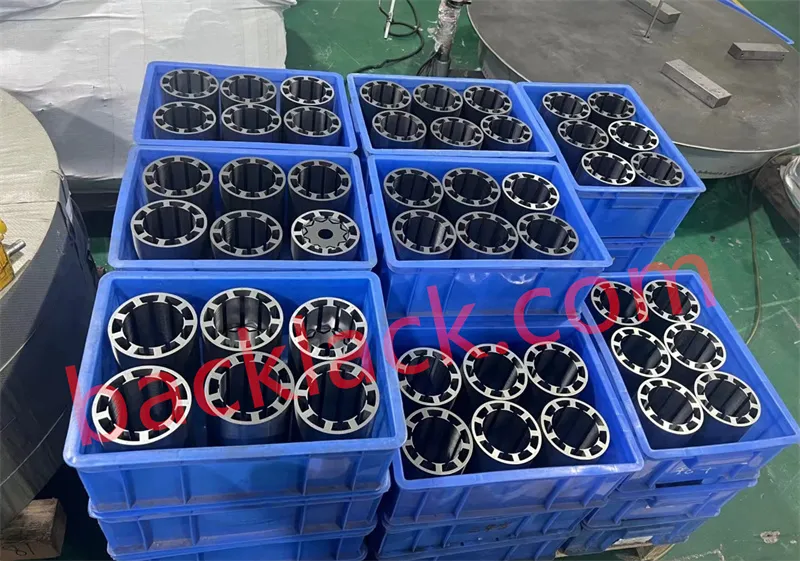
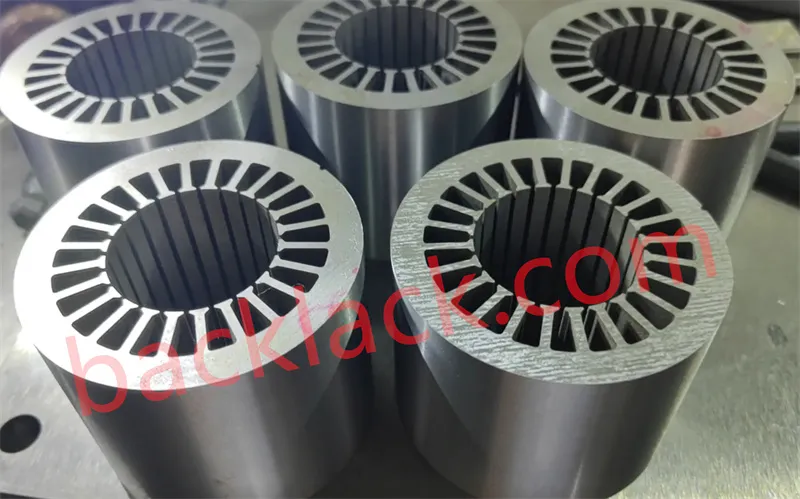
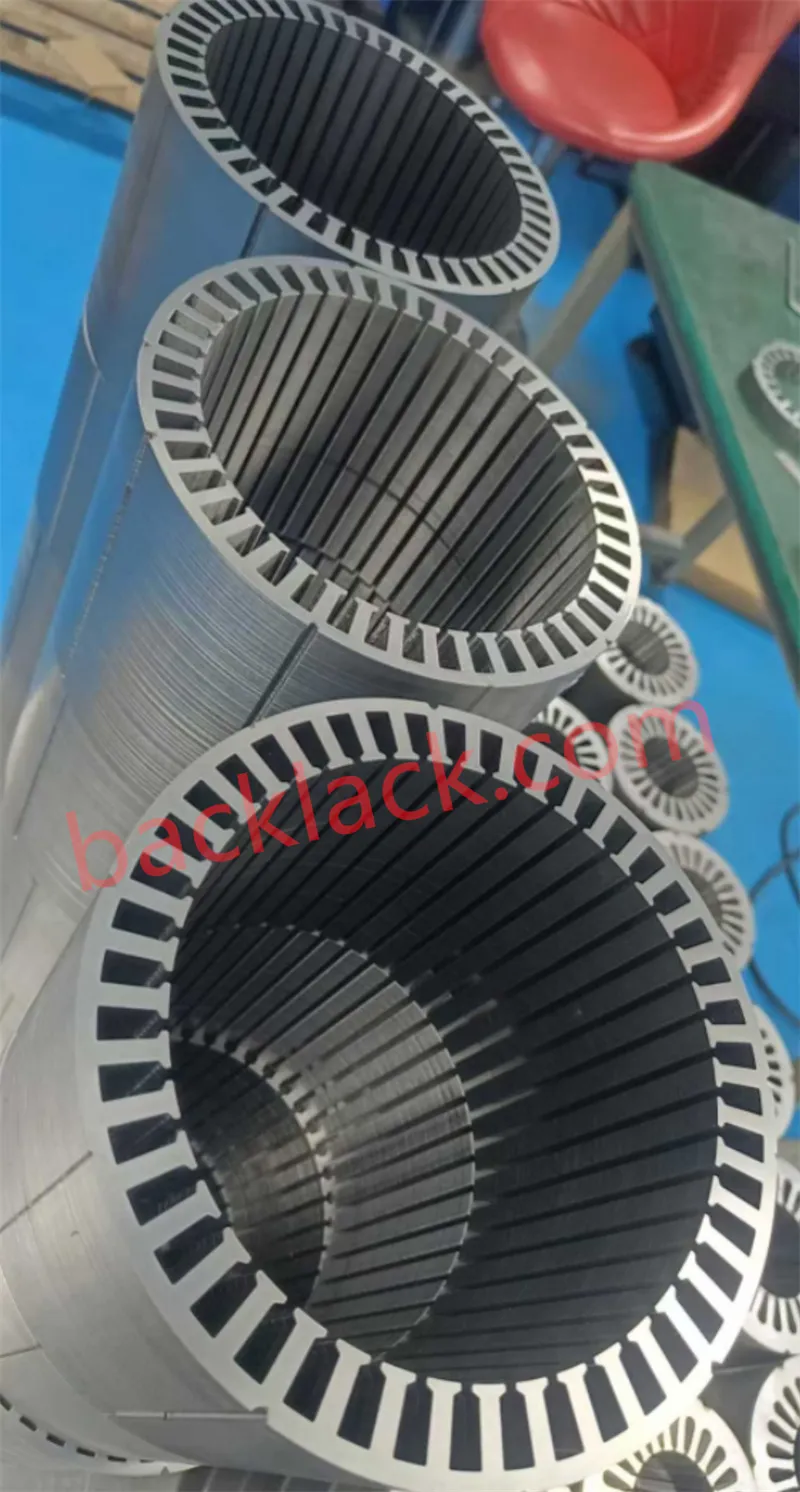
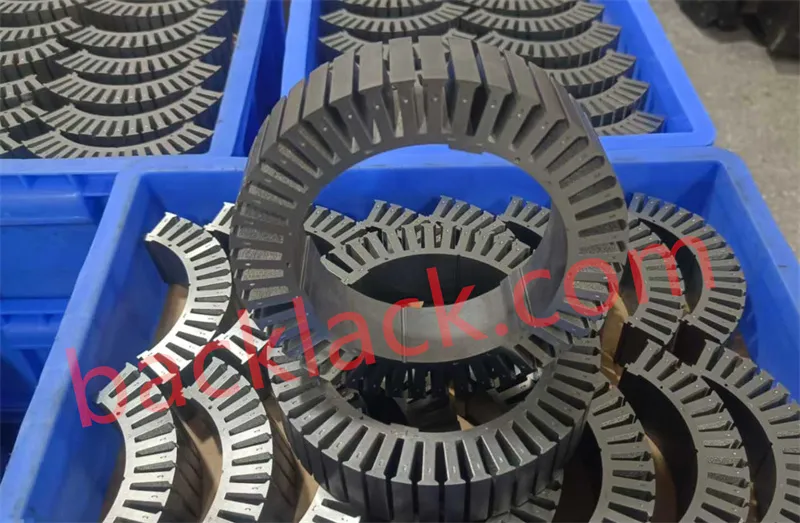
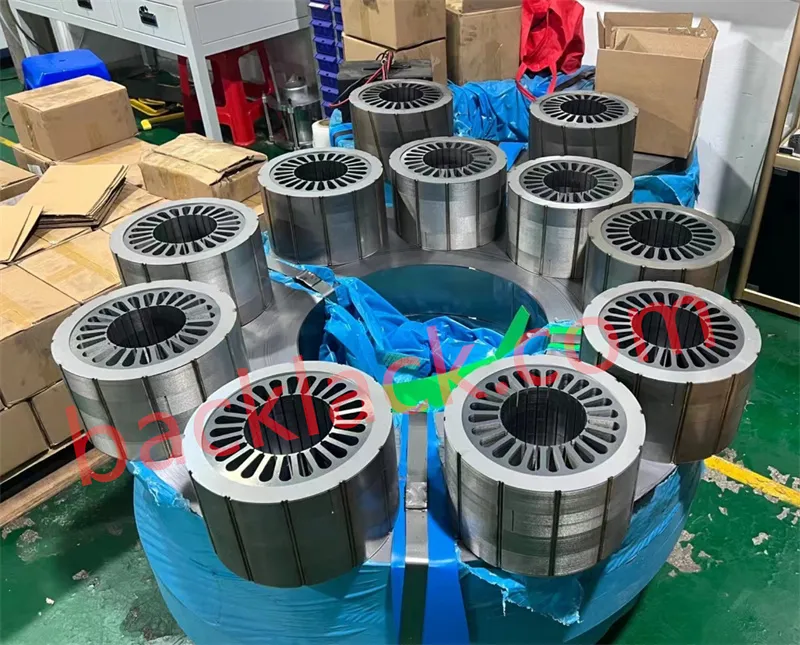
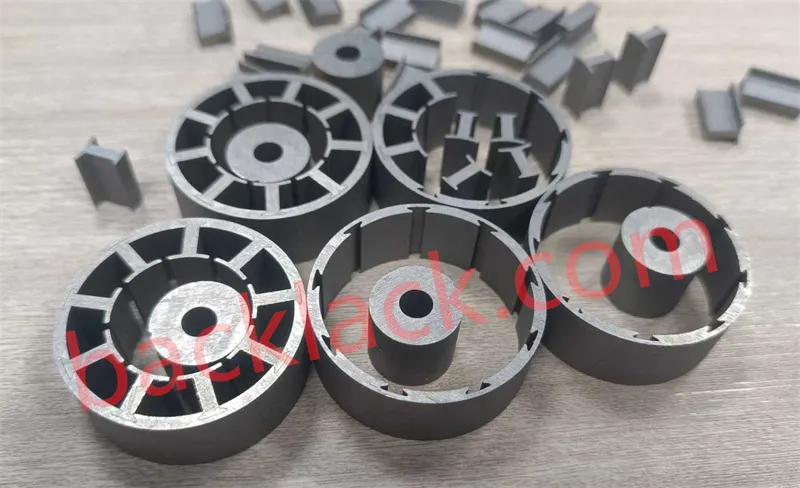
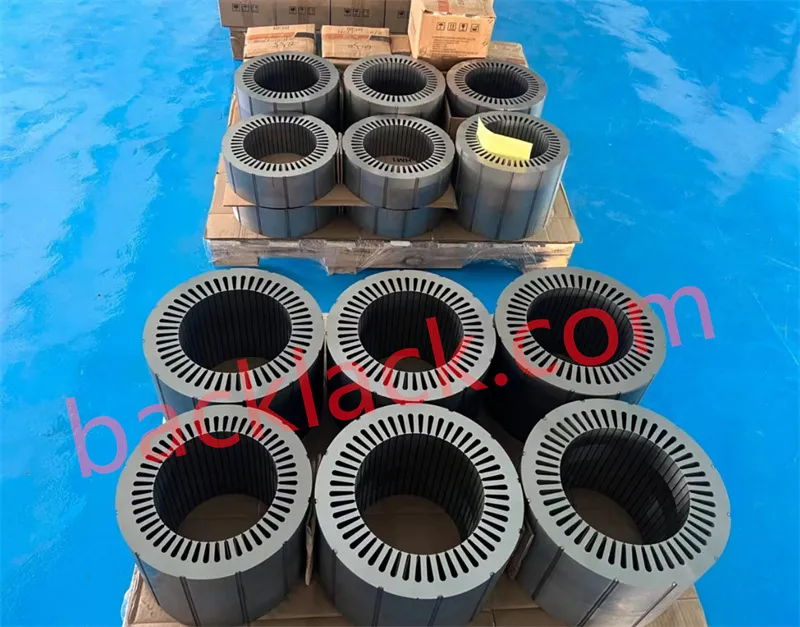
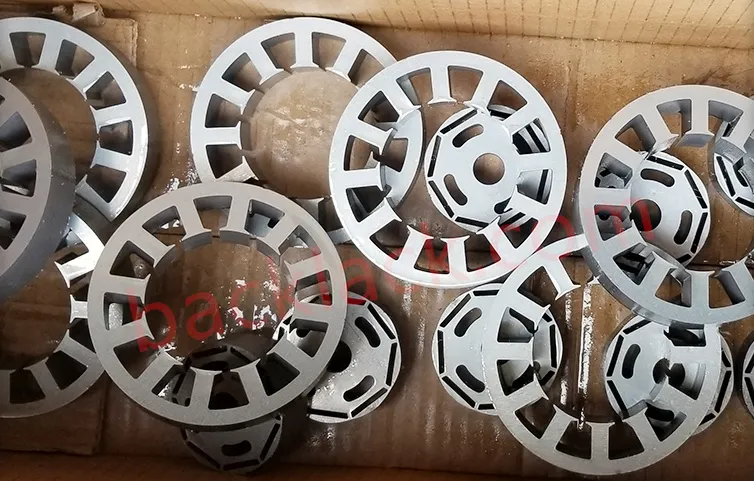
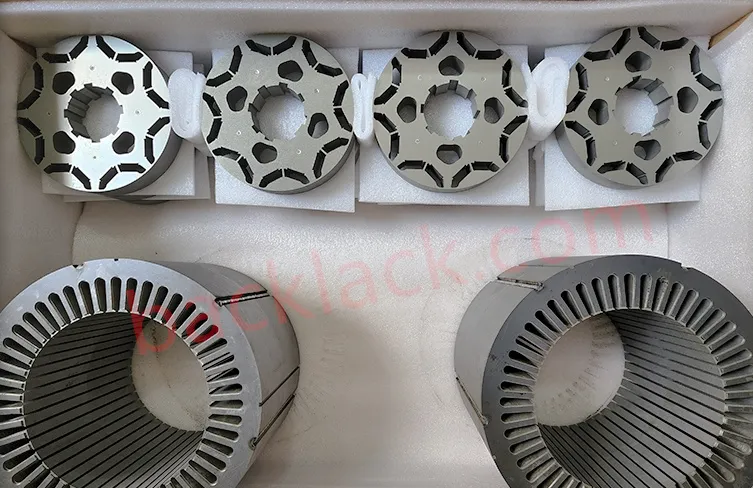










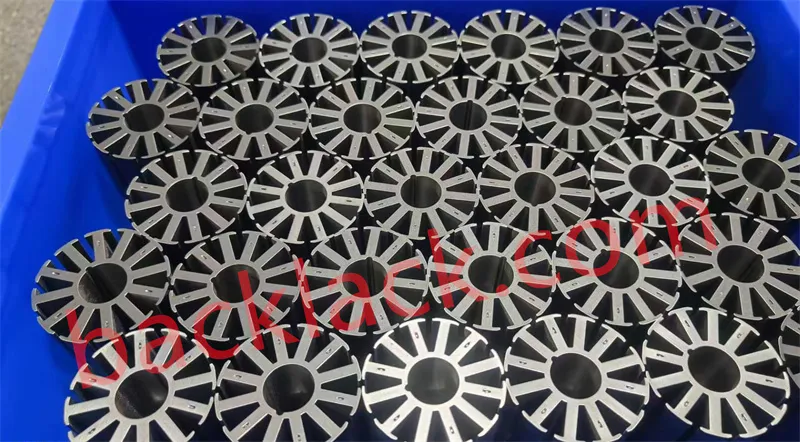




Four Core Competitive Advantages of Ultra-Thin Self-Adhesive Cores
Extreme High-Speed Adaptability & Mechanical Strength
The core forms a quasi-integral structure with interlamination bond strength of 5-25MPa, increasing overall rigidity by over 300%. Completely eliminates lamination expansion and deformation risks at 20,000+ RPM, preventing stator-rotor rubbing, and providing a reliability foundation for ultra-high-speed motors.
Significantly Reduced Iron Loss, Breaking Efficiency Limits
Completely eliminates mechanical stress damage and heat-affected zones caused by riveting/welding, preserving the optimal magnetic properties of silicon steel. Compared to traditional processes, iron loss is reduced by 20-35%, helping motors break through IE5 efficiency grades and significantly improving end-product energy efficiency and range.
Superior NVH Performance for "Silent" Drive
The adhesive layer acts as an efficient damping element, filling microscopic interlamination gaps and absorbing/buffering electromagnetic vibration energy. High-frequency electromagnetic noise is reduced by 6-10 dB(A), and RMS vibration acceleration is decreased by over 60%, providing a quiet and smooth experience for high-end applications.
Improved Thermal Uniformity & Heat Dissipation
The cured adhesive layer establishes an efficient "thermal bridge," reducing interlamination thermal resistance by 70%, allowing heat inside the core to be conducted quickly and evenly to the housing. Reduces local hot spot temperatures by 15-25°C, improving motor continuous power output capability and thermal reliability.
Technology Comparison: Self-Adhesive Cores vs. Traditional Cores
The following data, based on comparative testing of identical designs and material grades (20JNEH1200), reveals the comprehensive performance advantages of self-adhesive technology:
| Comparison Metric | Traditional Silicon Steel Core (Riveting/Welding) | Ultra-Thin Self-Adhesive/Bonded Core |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Fair, significant outer diameter expansion at high speed (85μm @20krpm) | Excellent, quasi-integral structure, minimal expansion (12μm @20krpm) |
| Iron Loss/Efficiency | Greatly affected by processing stress, typical value 6.8W/kg @1.5T/400Hz | Very Low, magnetic properties preserved, typical value 5.1W/kg @1.5T/400Hz |
| NVH Performance | Noise from interlamination micro-movement, vibration acceleration 2.8m/s² | Superior, damping reduces noise, vibration acceleration 1.1m/s² |
| Process Complexity | Requires additional riveting or welding steps after stamping, increasing cycle time | Simplified, direct stacking and single thermal curing after stamping, efficiency improved by 40% |
| Applicable Thickness | Difficult to rivet ultra-thin sheets (≤0.1mm), prone to deformation and tearing | Perfectly Compatible, specifically designed for 0.05-0.35mm ultra-thin silicon steel |
Materials & Processes: Dual Assurance for Extreme Performance
Material Revolution of Ultra-Thin Silicon Steel
Based on the physical principle that eddy current loss is proportional to the square of thickness, reducing silicon steel thickness from 0.35mm to 0.1mm can decrease eddy current loss to 1/4. We cooperate with top steel mills to develop specialized self-adhesive coated silicon steel, with a pre-coated 3-5 micron special formula epoxy-based adhesive on the substrate surface, achieving 10-25MPa interlamination bond strength after curing.
High-Precision In-Die Gluing Process
Our fifth-generation in-die gluing system achieves synchronous "stamp-and-bond" process, precisely applying adhesive dots to specified locations during high-speed stamping (120-200 strokes/minute), with positional repeatability accuracy of ±0.02mm and glue volume control accuracy of ±2%. For the vulnerable tooth area, patented dual-point reinforcement bonding technology is employed, applying adhesive dots simultaneously at the tooth tip and root to form a stable triangular structure, increasing tooth stiffness by 70-100%, perfectly withstanding the high assembly stress of hairpin windings.
Industry Applications: Customized Solutions
High-Speed Motor Spindles
Employs 0.1mm and below ultra-thin silicon steel with full-tooth gluing + outer circle auxiliary gluing scheme, ensuring dynamic balance accuracy and structural stability at 30,000-50,000 RPM.
Industrial Servo Motors
Uses 0.15-0.2mm materials with precise control of adhesive application volume, ensuring strength while minimizing the adhesive layer's impact on slot fill factor, meeting high power density and high dynamic response requirements.
New Energy Vehicle Traction Motors
Utilizes 0.2mm thick silicon steel paired with high-temperature resistant (180°C) adhesive, optimized tooth bonding to withstand hairpin winding assembly stress, ensuring long-term stability in oil-cooled environments, helping to increase power density and driving range.
UAV Motors
Addressing extreme lightweight needs, developed "Micro-Dot-Matrix" bonding technology—applying minimal adhesive only at key stress points to achieve the optimal balance between weight and strength, improving thrust-to-weight ratio.

About Youyou Technology
Youyou Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the manufacture of Self-bonding precision cores made of various soft magnetic materials, including Self-bonding silicon steel, ultra-thin silicon steel, and Self-bonding specialty soft magnetic alloys. We utilize advanced manufacturing processes for precision magnetic components, providing advanced solutions for soft magnetic cores used in key power components such as high-performance motors, high-speed motors, medium-frequency transformers, and reactors.
The company Self-bonding precision core products currently include a range of silicon steel cores with strip thicknesses of 0.05mm(ST-050), 0.1mm(10JNEX900/ST-100), 0.15mm, 0.2mm(20JNEH1200/20HX1200/ B20AV1200/20CS1200HF), and 0.35mm(35JNE210/35JNE230/ B35A250-Z/35CS230HF), as well as specialty soft magnetic alloy cores including Hiperco 50 and VACODUR 49 and 1J22 and 1J50.