Industry application cases

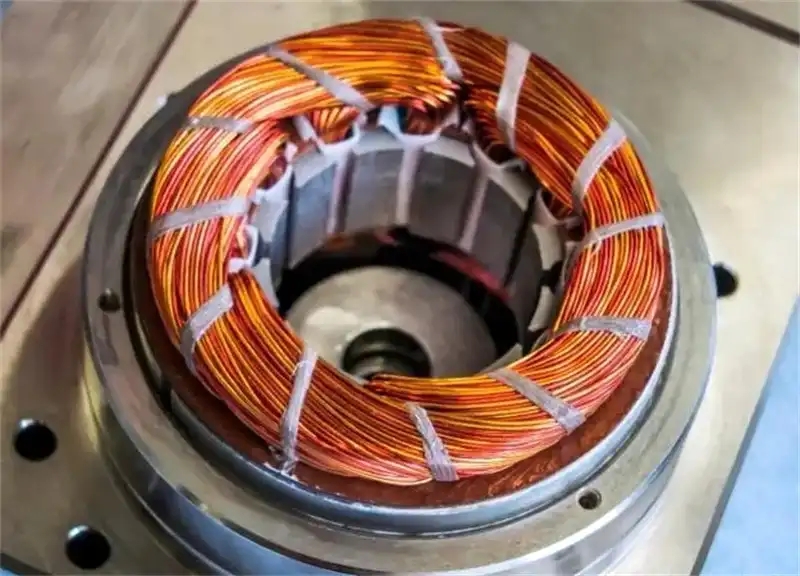
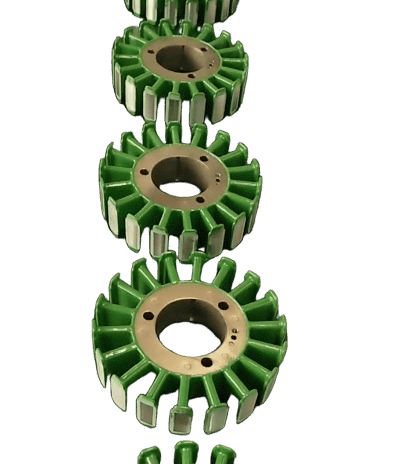
New energy vehicle motor
Tesla's drive motor uses bonding lamination technology to achieve higher torque density and heat dissipation efficiency.
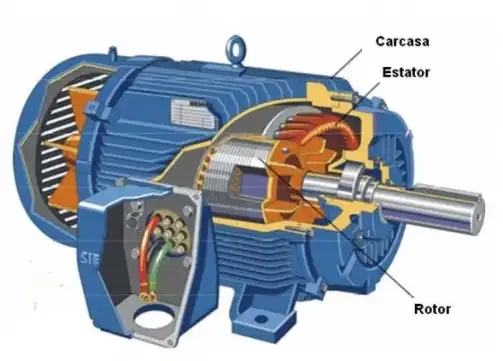
Industrial servo motor
ABB's SynRM (synchronous reluctance motor) reduces iron loss through bonding process and improves energy efficiency to IE5 standard.

Household appliances
The variable frequency air conditioner compressor motor significantly reduces operating noise due to bonding technology.