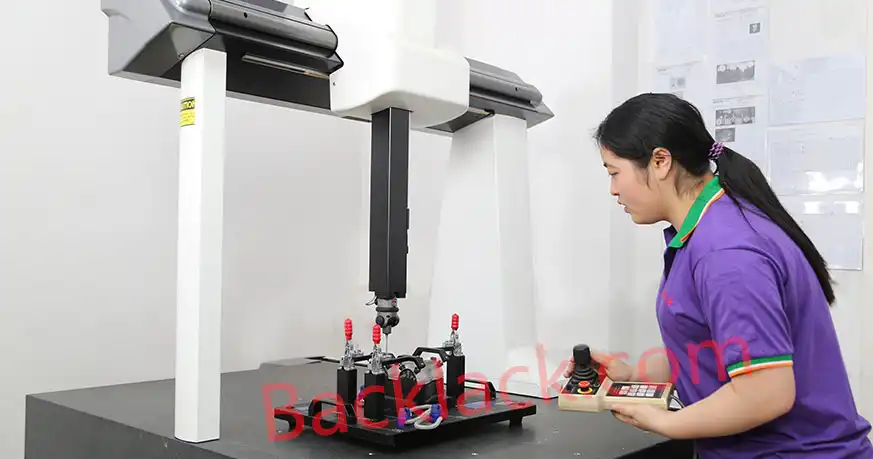
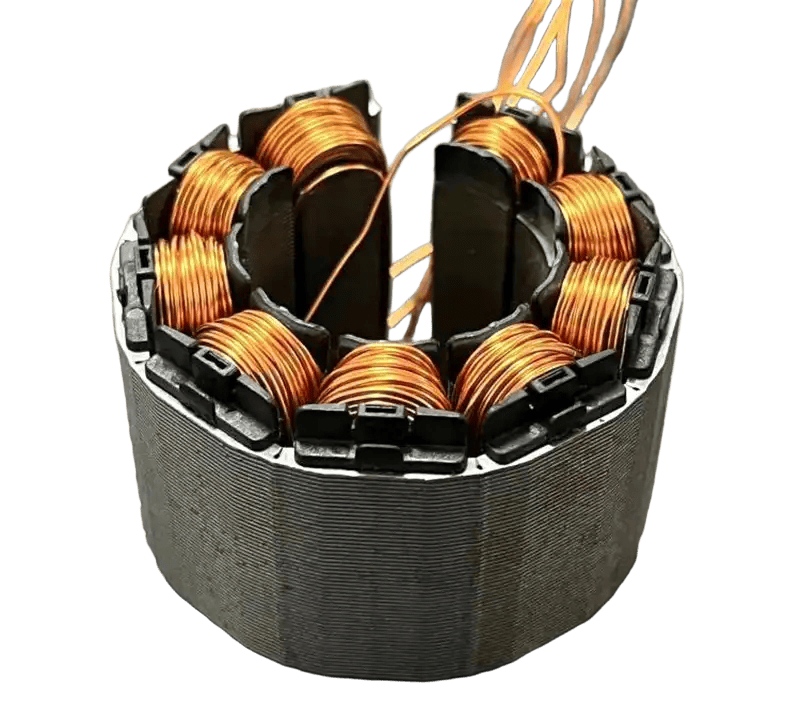
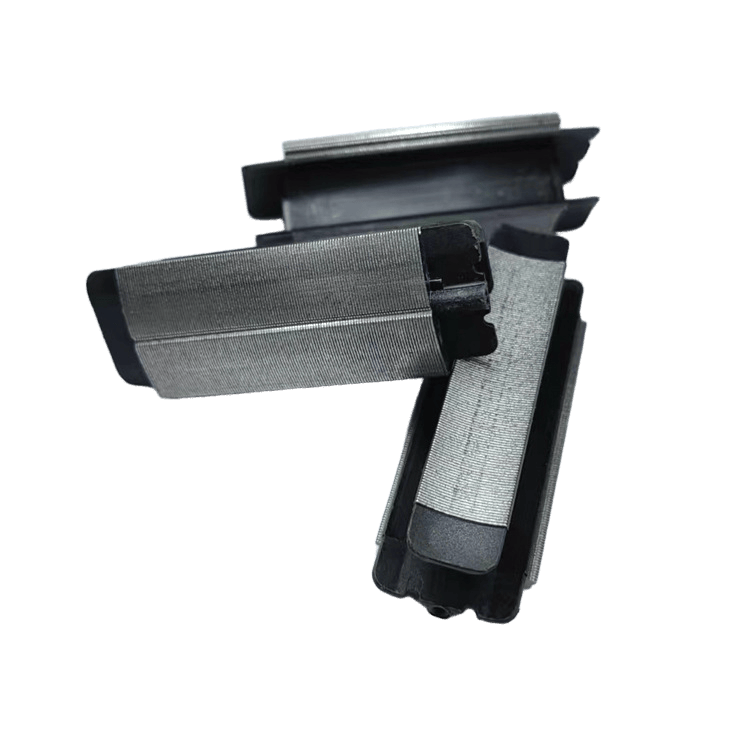
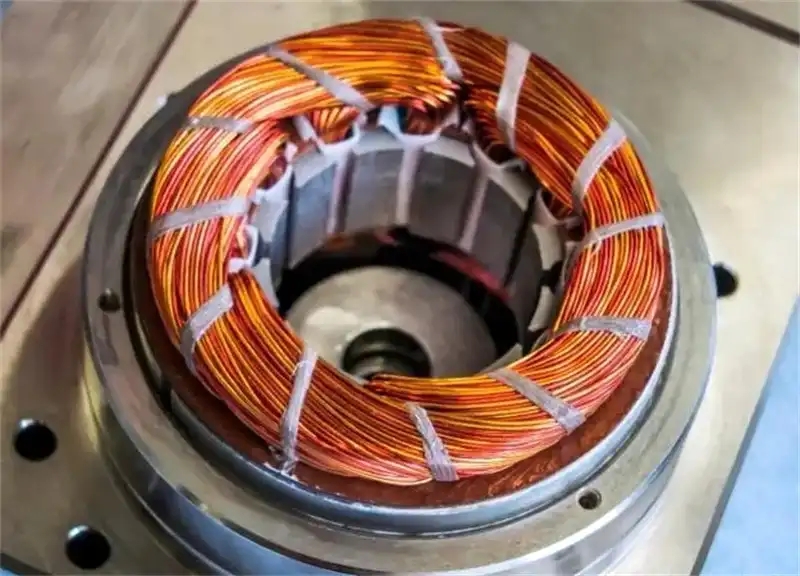
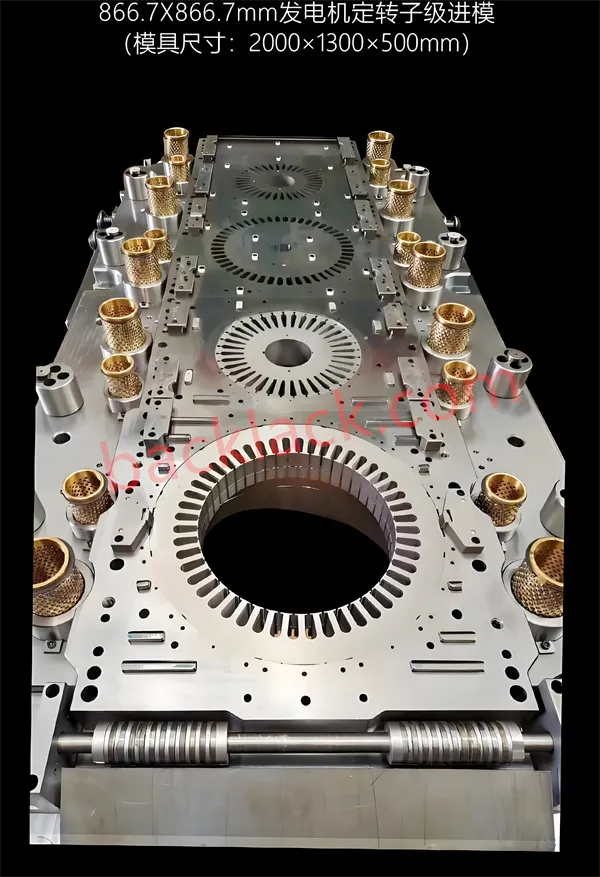
"Backlack is expensive—is it truly worth it?" This is the question I hear most from our clients. Today, I’ll break down the core technical and commercial logic of this technology from the perspective of the factory floor.
I. The Factory Advantage: Why Engineers Demand Backlack
1. "Damage-Free" Physical Performance
- Stress Elimination: Conventional clinching or interlocking creates significant local mechanical stress, degrading magnetic permeability. Backlack is a "stress-free" connection. Our tests show that core loss is reduced by 10% - 15% compared to traditional methods using the same steel grade.
- Superior Insulation: While welding destroys interlaminar insulation and creates short-circuit paths, Backlack forms a dense, continuous insulation layer (approx. 2-6 µm) after curing, completely eliminating interlaminar eddy currents.
2. High-Speed Structural Integrity
Once cured, the core becomes a monolithic block with shearing strengths often exceeding 20 MPa. This ensures that rotor laminations remain perfectly aligned even at extreme speeds of 20,000+ RPM. Furthermore, the full-surface bond provides natural protection against moisture and salt spray corrosion.
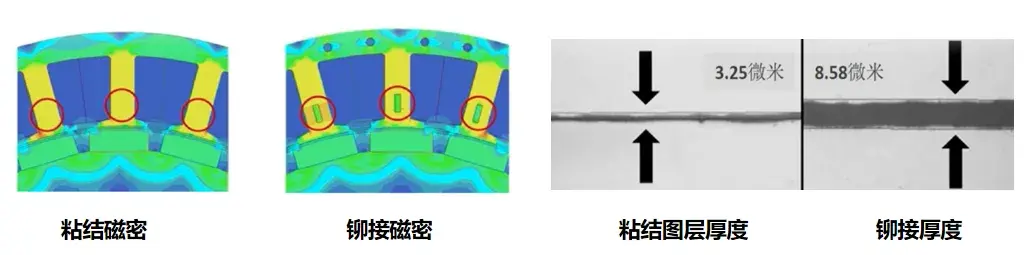
II. Factory Secrets: Mastering the "Three Devilish Details"
1. The "Pressure Balancing Act" During Curing
During the heating phase, the resin passes through a "glass transition" state where it flows like honey. If the pressure is too low, the bond fails; if too high, resin squeeze-out leads to dimensional inaccuracies. We utilize closed-loop servo-hydraulic controls to maintain thickness tolerances within ±0.05 mm.
2. Zero Tolerance for Burrs
In Backlack stacking, burrs are lethal. Because of the full-surface contact, even a 0.03mm burr can decrease the bonding area and dilute strength. We sharpen our progressive dies 1.5x more frequently than standard tools to keep burr heights strictly below 0.01 mm.
3. Thermal Uniformity Management
For large-diameter stators, temperature gradients between the ID and OD can cause uneven curing. Our facility employs Induction Heating combined with Mold Heat Transfer to ensure the entire core reaches the curing window simultaneously.
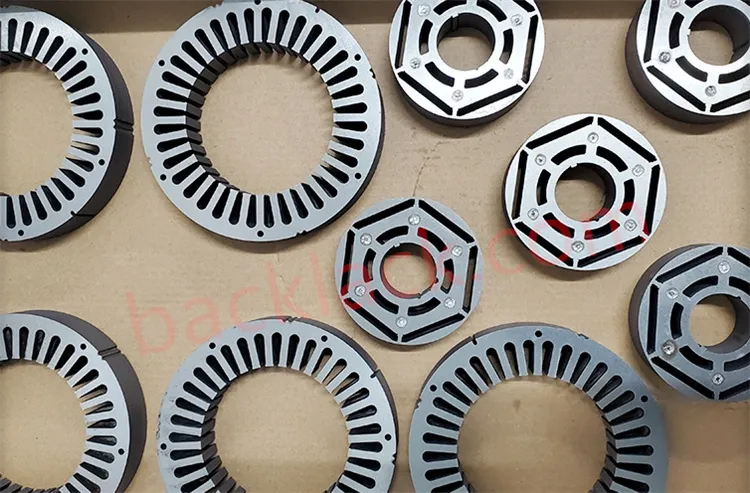
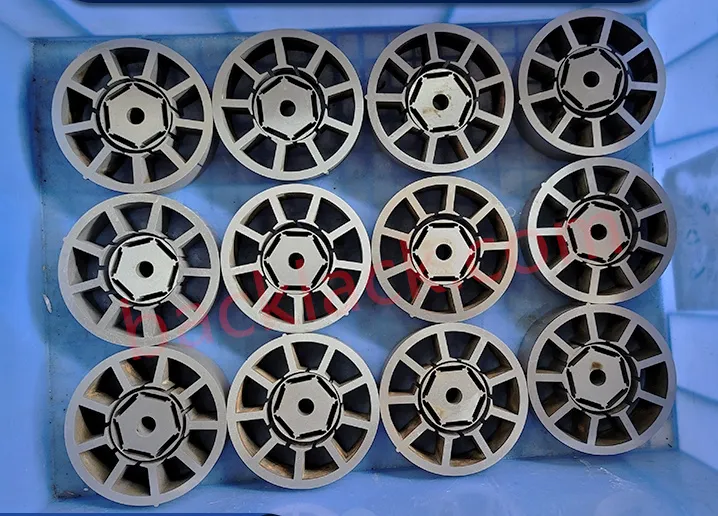
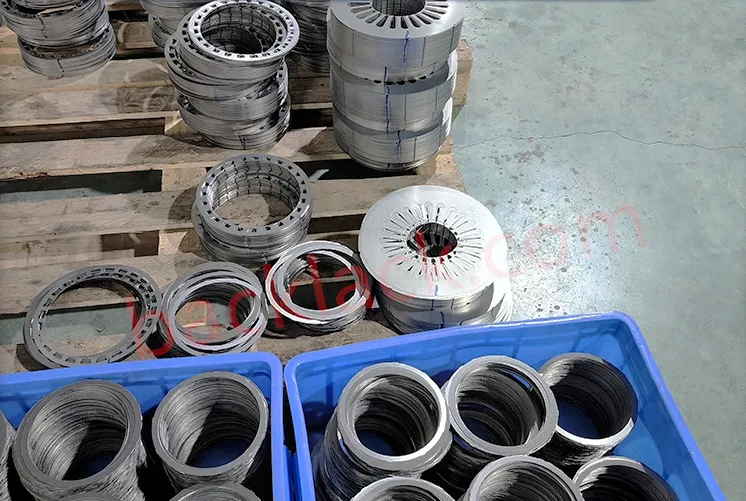
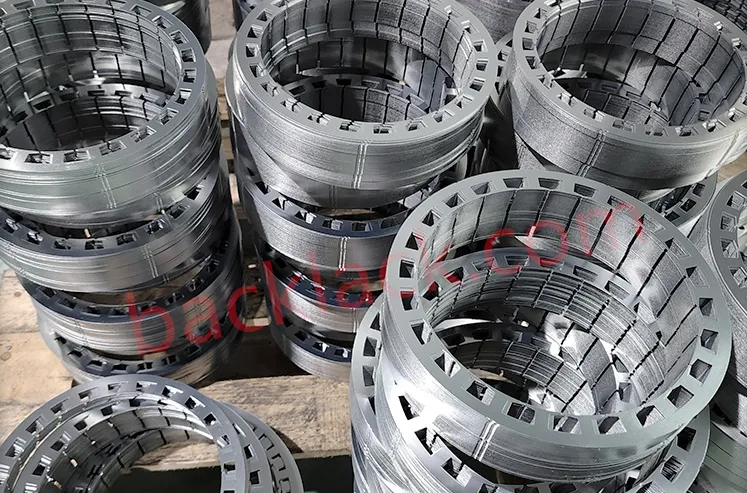
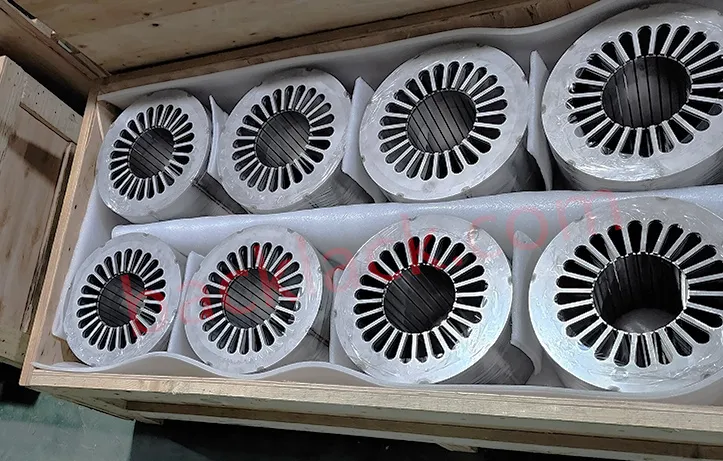
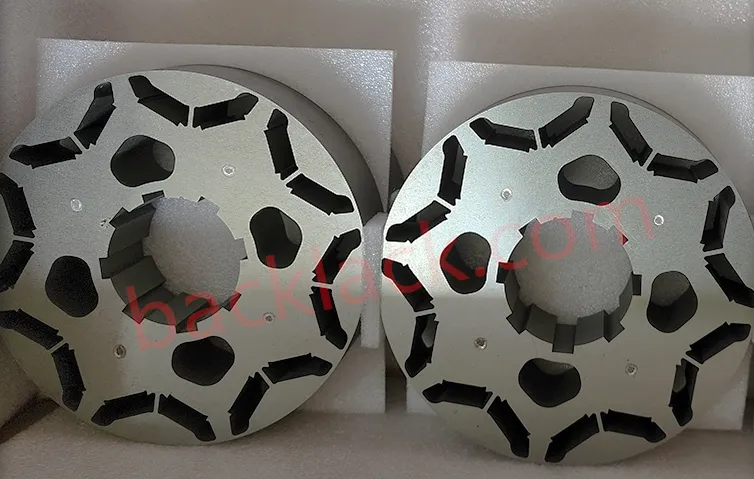
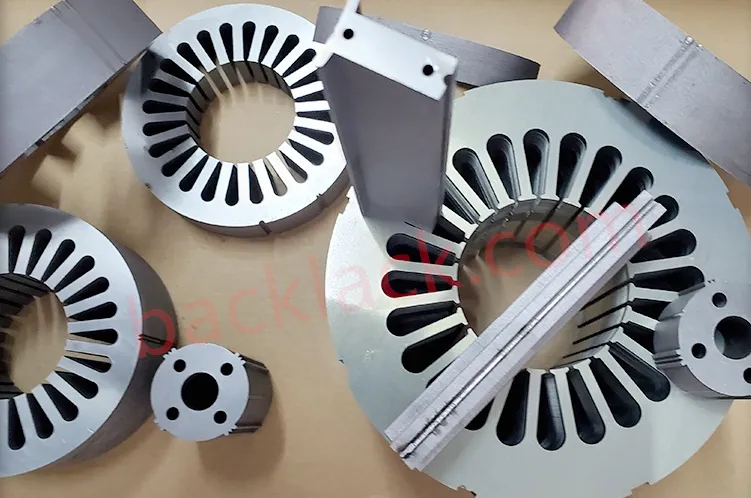
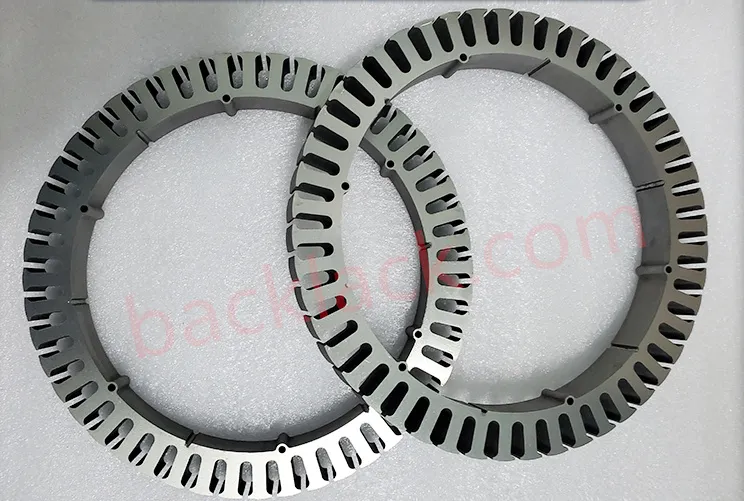
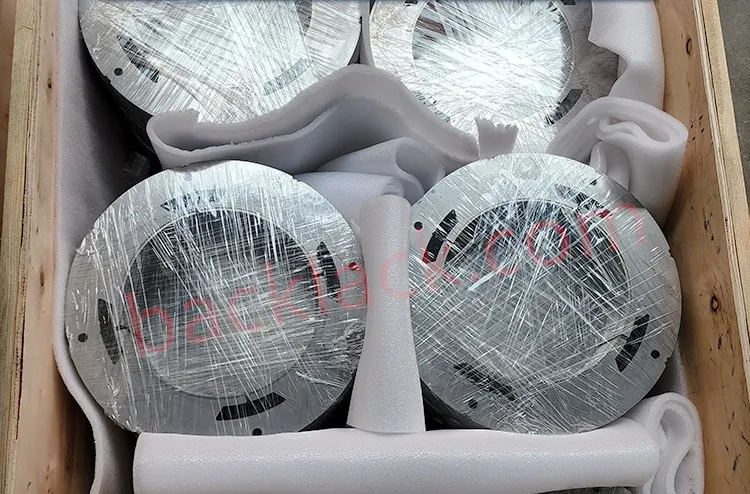
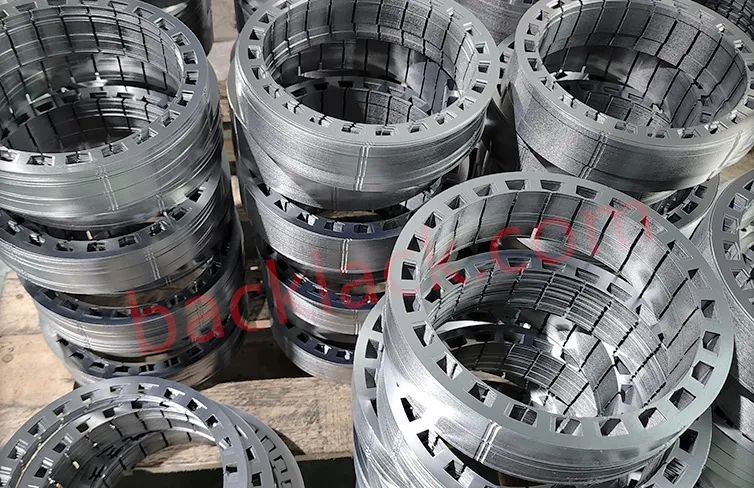
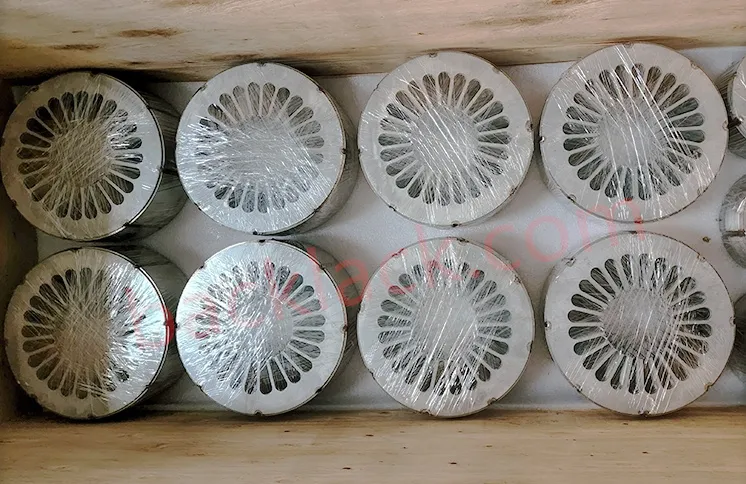
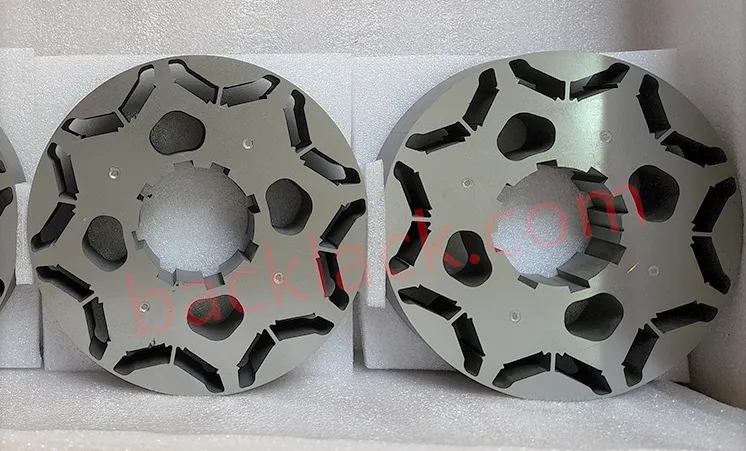
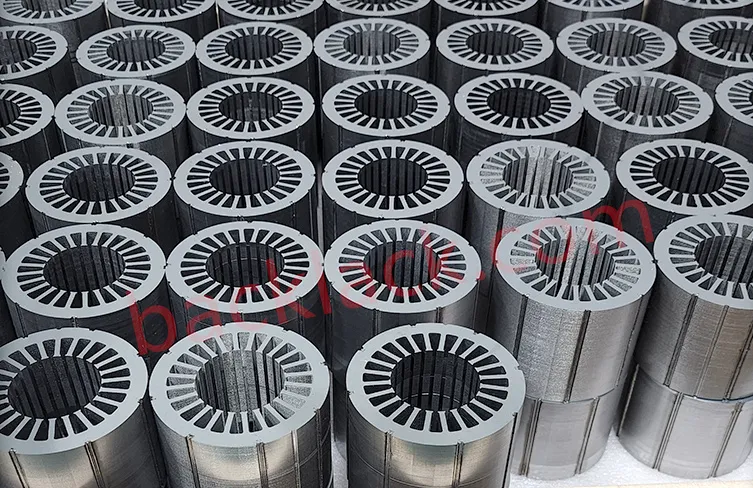
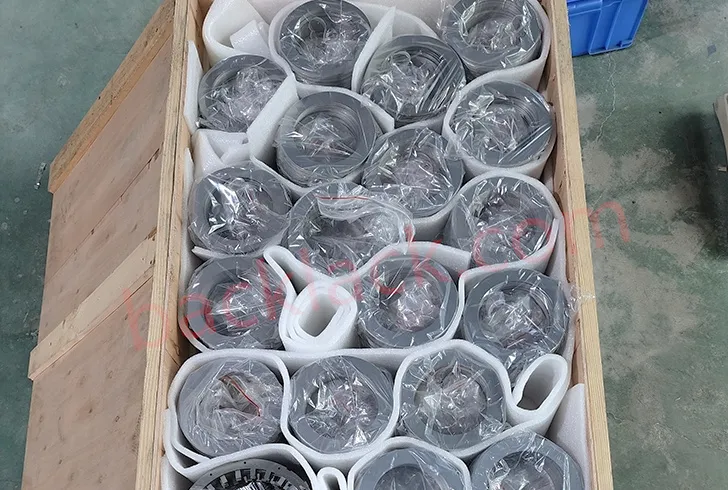








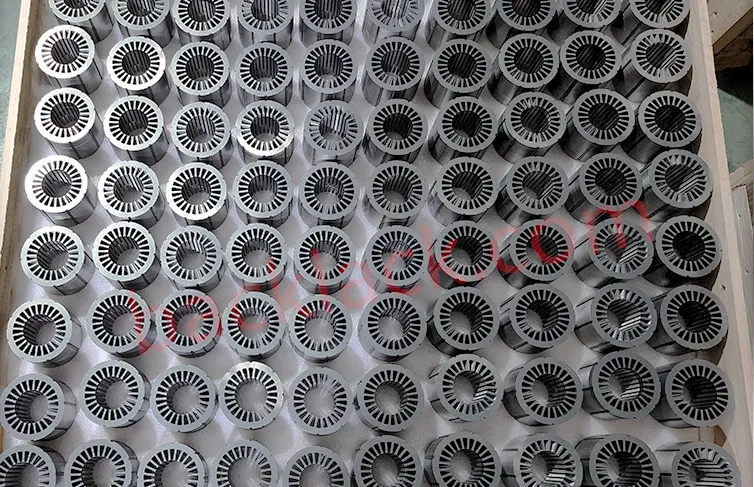


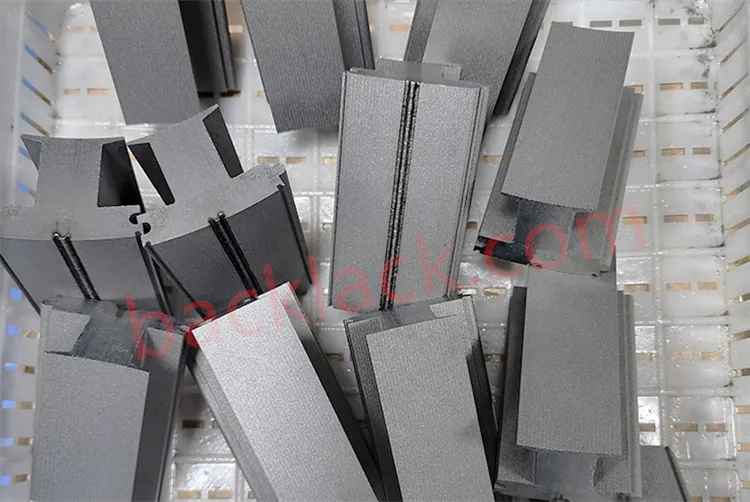








III. The Economic Reality: Is Backlack Actually More Expensive?
| Feature | Clinching / Welding | Backlack Self-Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Secondary Processing | Requires OD grinding (due to welding distortion) | No grinding required; achieves final dimensions out of the mold |
| Assembly Handling | Prone to "spring-back"; requires extra fixtures | Solid monolithic structure; handles like solid metal |
| Space Factor (Stacking Factor) | Lower (approx. 95-96%) | Ultra-high (can exceed 98%) |
| NVH Performance | Requires additional acoustic damping | Native noise reduction via high structural damping |
Conclusion: While the raw material cost is higher, the total system cost is often lower because you eliminate secondary grinding, reduce motor size, and achieve superior power density.
IV. Advice for Motor Designers
- Account for Expansion: Curing adds a slight thickness to the coating. Always verify "nominal stack height" with us during the design phase.
- Optimize Positioning Holes: Ensure at least three symmetrical alignment holes are included for high-precision curing fixtures.
- Coating Compatibility: Brands like EB 549 or Remisol have different curing profiles. Consult with us early to ensure compatibility with our production lines.
Looking for a manufacturing partner?
We provide full-link solutions from material selection (JFE, Baosteel) to final thermal curing.
Request a Technical ConsultationHave specific dimensions? Contact our technical team for the "Backlack Process Specification Manual" or to request a sample of our latest high-speed bonded rotors.
About Youyou Technology
Youyou Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the manufacture of Self-bonding precision cores made of various soft magnetic materials, including Self-bonding silicon steel, ultra-thin silicon steel, and Self-bonding specialty soft magnetic alloys. We utilize advanced manufacturing processes for precision magnetic components, providing advanced solutions for soft magnetic cores used in key power components such as high-performance motors, high-speed motors, medium-frequency transformers, and reactors.
The company Self-bonding precision core products currently include a range of silicon steel cores with strip thicknesses of 0.05mm(ST-050), 0.1mm(10JNEX900/ST-100), 0.15mm, 0.2mm(20JNEH1200/20HX1200/ B20AV1200/20CS1200HF), and 0.35mm(35JNE210/35JNE230/ B35A250-Z/35CS230HF), as well as specialty soft magnetic alloy cores including Hiperco 50 and VACODUR 49 and 1J22 and 1J50.